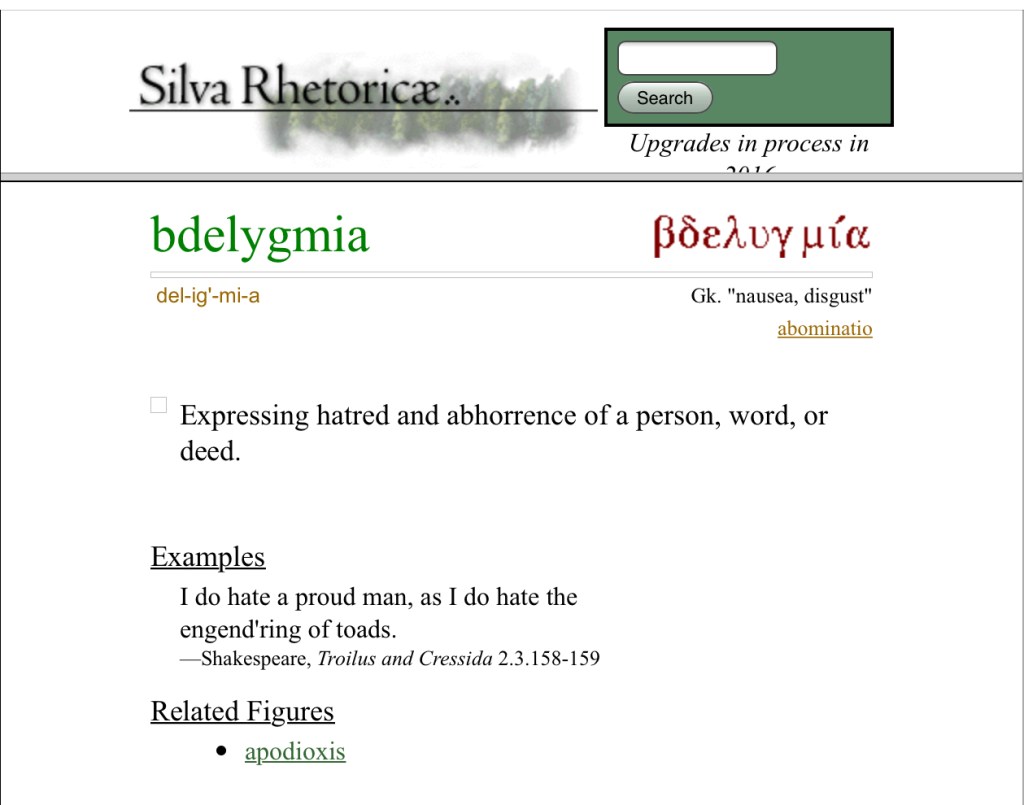
There are times when each of us needs to tell someone to go away. Adding a Shakespearean flavour to it lends both style and emphasis to any ejection of a bothersome person. It can also deliver a most satisfying sense of accomplishment to lovers of Shakespeare or of language in general.

The Problem of Female Agency in Shakespeare’s ‘The Taming of the Shrew’
Tweet
#women #Shakespeare #ShakespeareSunday
Begone is the base level entreaty for someone to leave. To say “Fellow, begone!” is the equivalent of “Okay mate, out you go…” today. If not addressing someone who is actually a fellow, you can use any other form of address, or simply say “Begone!” with an imperative tone. A flick of the hand toward the door could add a nice dramatic touch.
Get thee gone! adds a touch of urgency. It’s more like saying “Go, quickly!” or “Get out now!” This is used forty times throughout Shakespeare’s plays, usually when there is a sense of timeliness or hurry about the leaving. It can also suggest impatience or frustration with the person to whom the command is addressed.
In Henry IV part 1, Act 1 Scene 3, King Henry addresses Worcester thus:”Worcester, get thee gone, for I do seeDanger and disobedience in thine eye.”
In Act 3, Scene 1 of Timon of Athens, the grief-stricken Timon tells Alcibiades he wants to be left alone with the command “I prithee, beat thy drum and get thee gone.” This is a reference to the military practice of beating a particular rhythm for retreat, making it the Elizabethan equivalent of “beat it!”
In different parts of Henry 6 , we see Margaret of Anjou use Get thee gone in two different ways.
In part 2, Act 3 Scene 2, Margaret of Anjou farewells the Duke of Suffolk with an impassioned speech:
“O. let me entreat thee cease. Give me thy hand,
That I may dew it with my mournful tears;
Nor let the rain of heaven wet this place
To wash away my woeful monuments.
O, could this kiss be printed in thy hand.
That thou might think upon these by the seal,
Through whom a thousand sighs are breath’d for thee!
So get thee gone, that I may know my grief,
‘Tis but surmised whiles thou art standing by,
As one that surfeits thinking on a want.
I will repeal thee, or, be well assur’d,
Adventure to be banished myself;
And banished I am, if but from thee.
Go, speak not to me; even now be gone.”
In Act 3, Scene 6 of Henry 6 part 3, Margaret is far less heartbroken to be bidding her husband, King Henry VI, farewell. Furious and resentful at the amount of power he has given to his councillors– and her enemies– Warwick, Faulconbridge and York, Margaret announces her intention to summon her army and go to war with them. Henry begs her to “Stay, gentle Margaret, and let me speak.”
Her response is curt: “Thou has spoke too much already; get thee gone.”
Yet again, Shakespeare’s Margaret demonstrates that elementary truth: tone really is everything.

The Problem of Female Agency in Shakespeare’s ‘The Taming of the Shrew’
Tweet
#women #Shakespeare #ShakespeareSunday
Shakesepearean Ways To Tell Someone To Go Away
Tweet
#Shakespeare #words